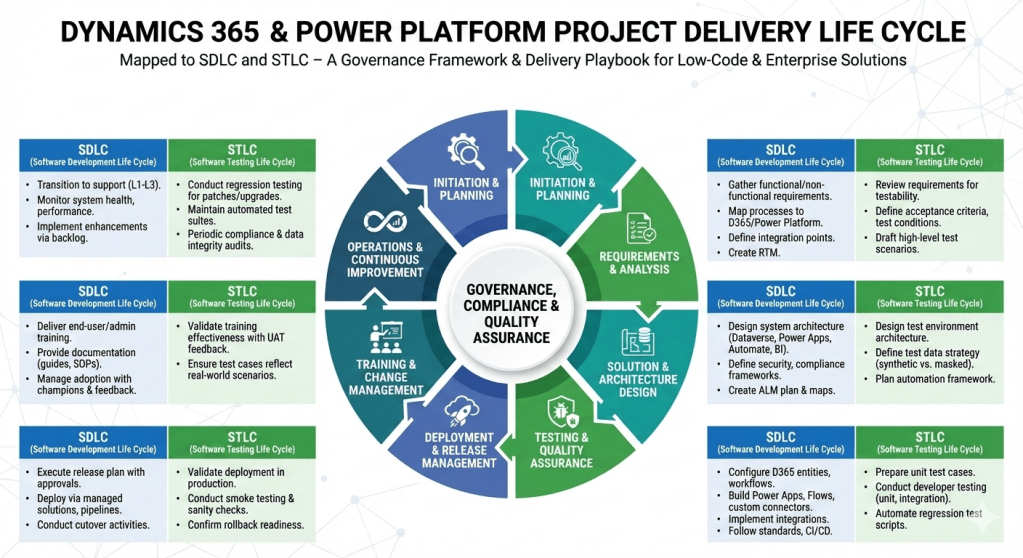
Here’s a step‑by‑step project delivery life cycle for Dynamics 365 & Power Platform projects, mapped to both SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) and STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle). I’ve structured it so you can use it as a governance framework or a delivery playbook.
Dynamics 365 & Power Platform Project Delivery Life Cycle
1. Initiation & Planning
- SDLC:
- Define business objectives, scope, and success criteria.
- Identify stakeholders, governance model, and compliance requirements.
- Conduct feasibility study and ROI analysis.
- STLC:
- Define test strategy aligned with business goals.
- Identify quality metrics, compliance standards, and risk areas.
2. Requirements & Analysis
- SDLC:
- Gather functional and non‑functional requirements (workshops, interviews, user stories).
- Map business processes to Dynamics 365 modules and Power Platform capabilities.
- Define integration points (ERP, CRM, CTI, external APIs).
- Create requirement traceability matrix.
- STLC:
- Review requirements for testability.
- Define acceptance criteria and test conditions.
- Draft high‑level test scenarios.
3. Solution & Architecture Design
- SDLC:
- Design system architecture (Dataverse, Power Apps, Power Automate, Power BI, Dynamics 365 modules).
- Define security, compliance, and governance frameworks.
- Create ALM (Application Lifecycle Management) plan with environments (Dev, Test, UAT, Prod).
- Prepare architecture maps and integration diagrams.
- STLC:
- Design test environment architecture.
- Define test data strategy (synthetic vs. masked production data).
- Plan automation framework (e.g., EasyRepro, Selenium, Power Automate test flows).
4. Development & Configuration
- SDLC:
- Configure Dynamics 365 entities, forms, workflows, and business rules.
- Build Power Apps (Canvas/Model‑Driven), Power Automate flows, and custom connectors.
- Implement integrations (Azure Functions, Logic Apps, APIs).
- Follow coding standards, version control (GitHub/Azure DevOps), and CI/CD pipelines.
- STLC:
- Prepare unit test cases.
- Conduct developer testing (unit, integration).
- Automate regression test scripts.
5. Testing & Quality Assurance
- SDLC:
- Conduct system testing, UAT, performance testing, and security validation.
- Validate integrations and data migration.
- STLC:
- Test Planning: Finalize test plan, entry/exit criteria.
- Test Design: Create detailed test cases, test scripts, and data sets.
- Test Execution: Run functional, regression, performance, and security tests.
- Defect Management: Log, track, and resolve defects in Azure DevOps/Jira.
- Test Closure: Document results, lessons learned, and sign‑off.
6. Deployment & Release Management
- SDLC:
- Execute release plan with governance approvals.
- Deploy via managed solutions, pipelines, or release automation.
- Conduct cutover activities (data migration, user provisioning, environment setup).
- STLC:
- Validate deployment in production.
- Conduct smoke testing and sanity checks.
- Confirm rollback strategy readiness.
7. Training & Change Management
- SDLC:
- Deliver end‑user training, admin training, and governance workshops.
- Provide documentation (user guides, SOPs, governance playbooks).
- Manage adoption with change champions and feedback loops.
- STLC:
- Validate training effectiveness with UAT feedback.
- Ensure test cases reflect real‑world scenarios.
8. Operations & Continuous Improvement
- SDLC:
- Transition to support (L1, L2, L3).
- Monitor system health, performance, and compliance.
- Implement enhancements via backlog grooming.
- STLC:
- Conduct regression testing for patches and upgrades.
- Maintain automated test suites for continuous validation.
- Periodic audits for compliance and data integrity.
This framework ensures governance, compliance, and quality assurance are embedded throughout delivery. It’s especially powerful for Dynamics 365 & Power Platform projects where configuration, low‑code development, and integrations coexist with enterprise‑grade testing.